Introduction:
Nestled atop a hill in Telangana, the Phanigiri Buddhist Site is a captivating archaeological treasure that provides a profound glimpse into the ancient Buddhist world. Situated approximately 45 kilometers from Suryapet District, 110 kilometers from Hyderabad via Bhuvanagiri, and 6 kilometers from Tirumalagiri, this site stands as a significant testament to the rich heritage and artistic achievements of early Indian Buddhism. Dating back to the 2nd–3rd centuries A.D. during the Satavahana and Ikshvaku periods, Phanigiri features an impressive array of ruins, including a majestic Mahastupa, apsidal chaityagrihas, life-size stucco sculptures, and rare octagonal stupas.Phanigiri’s artifacts, like Brahmi inscriptions and limestone panels, reflect its historical significance and the ongoing preservation efforts.
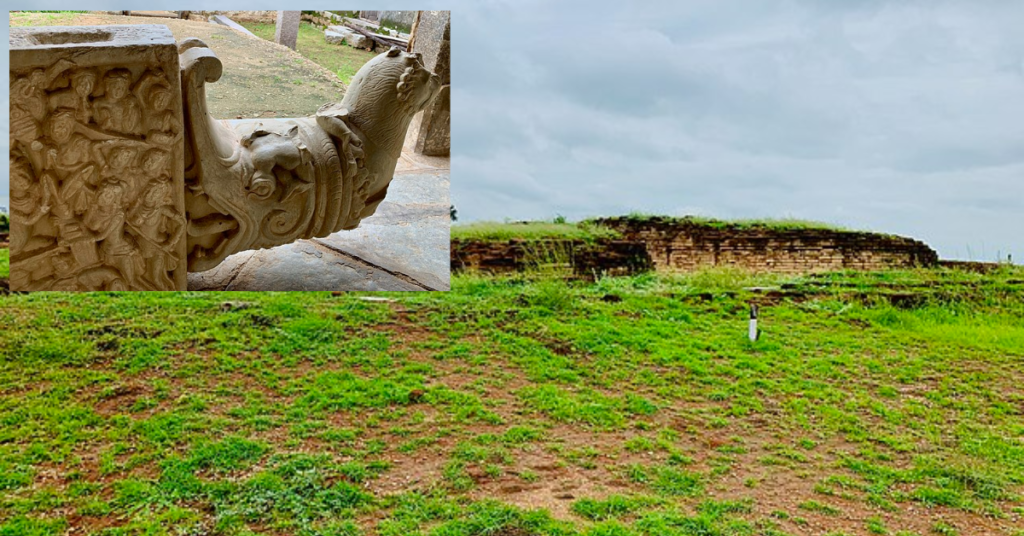

Location and Accessibility of Phanigiri Buddhist Site
Phanigiri, a notable Buddhist site, is on a hilltop in Telangana, 45 km from Suryapet, 110 km from Hyderabad, and 6 km from Tirumalagiri. Its elevated position provides a commanding view of the landscape and underscores its historical and spiritual significance.
Also read: Discovering the Rich History of the Chaya Someswara Temple
Historical Significance of Phanigiri Buddhist Site
Phanigiri is renowned for its extensive Buddhist ruins, which date back to the Satavahana and Ikshvaku periods (2nd–3rd century A.D.).The site reflects the flourishing of Buddhism in the region during this era. First, it highlights the widespread influence of Buddhist practices and, equally important, the architectural advancements of the time. Next, the artifacts discovered further illustrate the depth of Buddhist culture. Moreover, the detailed inscriptions and sculptures provide additional evidence of the period’s spiritual significance.
Finally, the overall findings underscore the site’s role in showcasing the era’s vibrant Buddhist heritage.Excavations at Phanigiri by the State Archaeology Department unveiled artifacts that shed light on ancient India’s rich Buddhist heritage.
Major Discoveries in Phanigiri Buddhist Site:
- Mahastupa: A large central stupa, likely a reliquary mound, used to house relics of the Buddha or revered monks. This stupa is a focal point of the site’s religious significance.
- Chaityagrihas and Viharas: The site contains apsidal chaityagrihas (prayer halls) and congregation hall viharas (monastic residences). These structures highlight the architectural and communal aspects of early Buddhist monastic life.
- Votive Stupas: Small stupas found at the site, typically erected by devotees to commemorate significant events or acts of piety.
Also read: Pandavula Gutta: The Hidden Prehistoric Gem of Telangana
- Life-size Stucco of Bodhisattva: An impressive stucco Bodhisattva, symbolizing a being seeking enlightenment to help others, highlights the period’s artistic achievements.
- Octagonal-shaped Stupa: A rare octagonal stupa at Phanigiri, distinct from typical circular ones, showcases architectural experimentation of the 2nd–3rd centuries A.D.
- Brahmi Inscriptions: Inscriptions in Brahmi script from the Satavahana and Ikshvaku periods offer valuable historical and chronological information about the site and its patrons.
- Coins: The site has yielded a variety of ancient coins, including punch-marked coins and those issued by the Kshatrapas, Romans, and Mahatalavara chiefs, revealing the economic interactions and influences of the time.
- Limestone Sculptural Panels: The panels at Phanigiri feature Buddha’s life events, Jataka tales, Buddhapada slabs, and images of Buddha and Bodhisattvas.
Restoration and Conservation
The exposed structures at Phanigiri need restoration and conservation efforts to preserve their historical and cultural integrity. Plans are underway to restore these ancient structures and to display the valuable Buddhist sculptures and artifacts in a museum, allowing visitors and scholars to appreciate the site’s historical significance fully.
Importance and Legacy
Phanigiri stands as a testament to the rich Buddhist heritage of ancient India. The site’s comprehensive range of structures and artifacts provides a unique window into the religious, cultural, and artistic achievements of the time. Its preservation is crucial for understanding the historical spread of Buddhism and the architectural innovations of the period.
In summary, the Phanigiri Buddhist site offers a profound glimpse into early Buddhist civilization through its extensive ruins, inscriptions, and sculptures. First, the site reveals a wealth of historical artifacts. Next, the intricate inscriptions provide insights into the Buddhist practices of the era. Furthermore, the sculptures showcase the artistic achievements of ancient craftsmen. Besides, the extensive ruins highlight the architectural sophistication of the time. Moreover, the site’s continued preservation efforts are equally important in maintaining its historical significance. Finally, Phanigiri stands as a testament to the rich cultural heritage of early Buddhism, offering a comprehensive understanding of its civilization.
The ongoing efforts to restore and conserve the site will ensure that its legacy continues to illuminate the history of Buddhism in India.
Also read: Yadagirigutta temple hidden secrets for tourists
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Phanigiri Buddhist Site stands as a remarkable window into the ancient Buddhist world, showcasing the architectural and artistic brilliance of the 2nd–3rd centuries A.D. First, with its imposing Mahastupa, Phanigiri reveals the depth of Buddhist devotion. Moreover, the rare octagonal stupa, distinct from typical circular ones, highlights the architectural experimentation of the time. In addition, the exquisite limestone sculptures demonstrate the sophistication of early Indian craftsmanship. Furthermore, these features collectively underscore the site’s historical significance, making it an invaluable treasure for understanding ancient Buddhist art and architecture.
The site’s rich collection of Brahmi inscriptions, ancient coins, and detailed relief panels further underscores its historical significance and cultural heritage. Moreover, these artifacts highlight the depth of its past. In addition, they offer valuable insights into the region’s artistic and historical developments. Furthermore, the detailed relief panels and inscriptions reveal the sophisticated craftsmanship of the era. Finally, this comprehensive assemblage of artifacts enhances our understanding of the site’s cultural and historical context. As restoration and conservation efforts continue, Phanigiri’s legacy as a vital center of Buddhist art and architecture will be preserved, offering future generations a profound understanding of India’s spiritual and artistic past.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Answer: The Mahastupa at Phanigiri is a large reliquary mound central to the site, likely used to house relics of the Buddha or revered monks, underscoring its religious importance.
Answer: Phanigiri is home to a rare octagonal-shaped stupa, differing from the more common circular stupas, reflecting the architectural experimentation and innovation of the period.
Answer: Excavations have unearthed Brahmi inscriptions, ancient coins from various cultures, life-size stucco sculptures, and intricate limestone panels depicting significant events from the life of the Buddha and Jataka tales.
Answer: Phanigiri is located approximately 45 km from Suryapet District, 110 km from Hyderabad via Bhuvanagiri, and 6 km from Tirumalagiri, making it accessible by road from these locations.
Answer: Ongoing restoration and conservation efforts aim to preserve the exposed structures and valuable artifacts, with plans to display these in a museum to highlight the site’s historical and cultural significance.