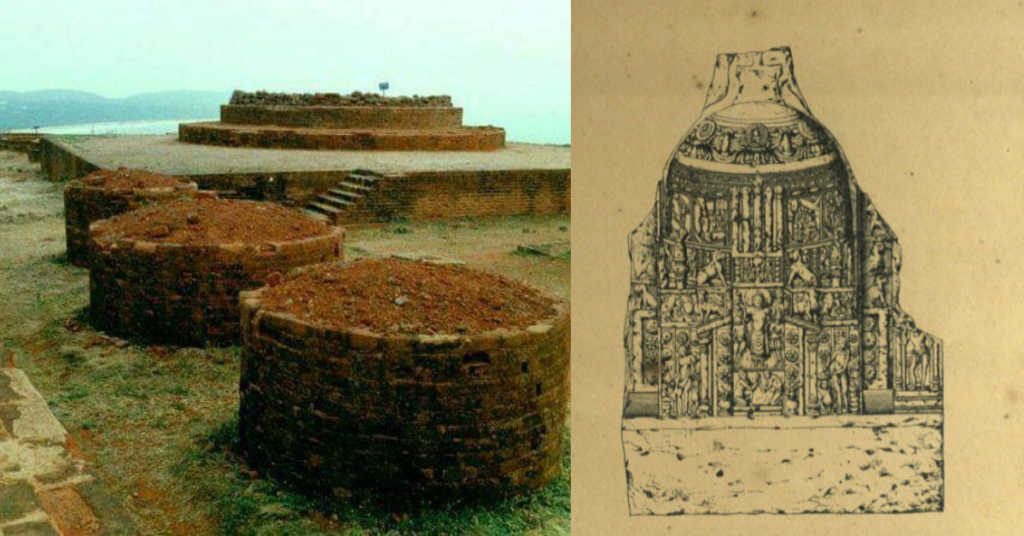
The Bhattiprolu Stupa is an ancient Buddhist monument in the Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh, India. It is also known as the “Mahachaitya” and is one of the earliest and most important Buddhist stupas in South India. Discovered in 1870 and excavated in 1892 by British archaeologist Alexander Rea, this stupa holds great historical and religious significance.
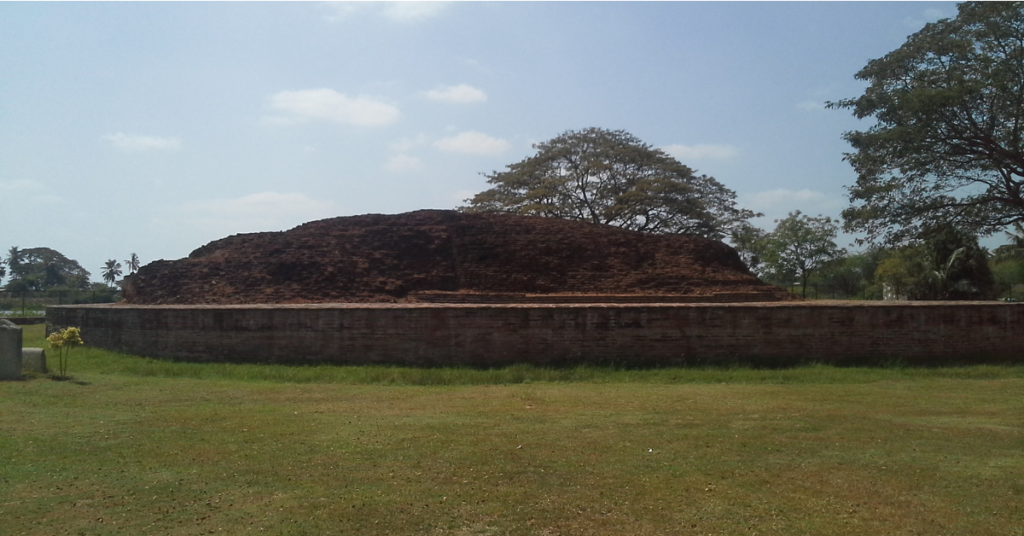

Historical Background of Bhattiprolu Stupa
The Bhattiprolu Stupa dates back to the 3rd century BCE, during the reign of Emperor Ashoka, who was instrumental in the spread of Buddhism across India and beyond. Ashoka built numerous stupas to commemorate significant events in the life of Buddha and to house relics. The Bhattiprolu Stupa is believed to have been constructed to enshrine the remains of Buddhist monks and other important relics.
This stupa is also linked to the ancient trade routes that connected various parts of India and facilitated the spread of Buddhism. As a result, it attracted many pilgrims and traders, making it a vital center for cultural exchange.
Also Read: Bavikonda Exploring the Rich Heritage of an Ancient Buddhist Monastery
The Stupa’s Structure and Architecture
The Bhattiprolu Stupa is an impressive example of ancient Indian architecture. Originally, it was built in a hemispherical shape, a common design for stupas. The stupa was made from brick and stood at a considerable height. Over the years, the structure has suffered due to natural wear and tear, but the remains still reflect its grandeur.
The stupa is adorned with intricate carvings and inscriptions that provide valuable insights into the art and culture of the time. Some carvings depict scenes from the Jataka tales, which narrate the previous lives of Buddha. The inscriptions, written in Brahmi script, offer historical context and information about the patrons and builders of the stupa.
Significance of Bhattiprolu Brahmi Script

One of the most fascinating aspects of Bhattiprolu is its connection to the evolution of the Brahmi script. The inscriptions found at the site are in a form of Brahmi script that is distinct from the Ashokan Brahmi found in other parts of India. This unique variant is referred to as the Bhattiprolu script. It is considered the precursor to the Telugu-Kannada script used in South India today.
The discovery of these inscriptions was a breakthrough in the study of South Indian languages. It established Bhattiprolu as one of the earliest centers of writing in the region. The Bhattiprolu script helped pave the way for the development of various South Indian scripts. Its importance in epigraphy and linguistics cannot be overstated.
Also Read: SriMukhalingam Temple: The Powerful Varanasi of South India
Cultural and Religious Impact
The Bhattiprolu Stupa was a major pilgrimage site for Buddhists in ancient India, drawing monks, scholars, and devotees from across the region. Its role as a religious center contributed to the spread of Buddhist teachings and practices in South India. The stupa’s architectural style also influenced other Buddhist monuments in the region, contributing to the unique identity of South Indian Buddhist art and architecture.
The influence of the stupa extended beyond religion. The Bhattiprolu inscriptions played a key role in shaping the linguistic landscape of South India, making the site a cornerstone of not just religious but also cultural history.
Rediscovery and Archaeological Excavations
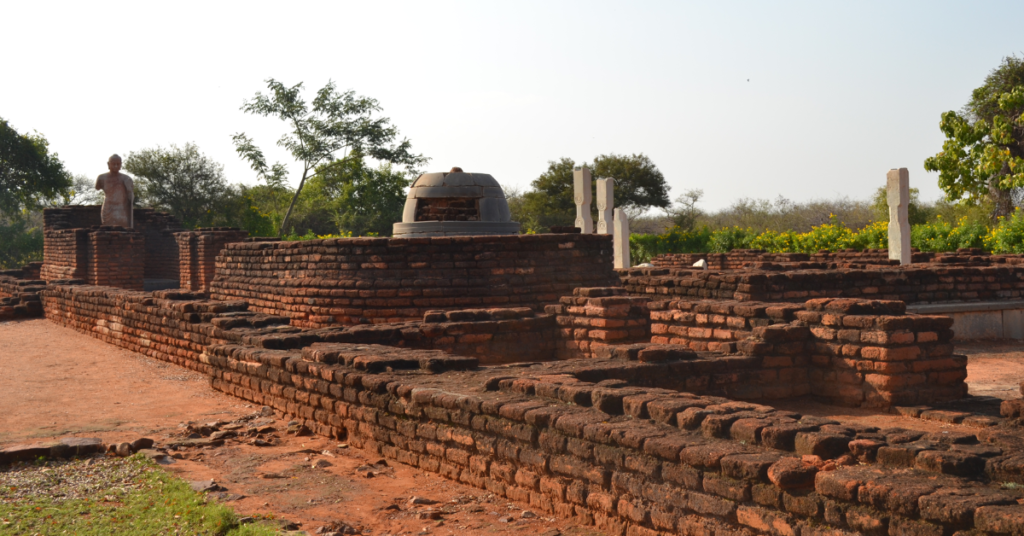

The Bhattiprolu Stupa was largely forgotten for centuries, buried under layers of history. It was rediscovered in the 19th century during British-led archaeological expeditions in the region. Noted archaeologist Robert Sewell first reported the site in the late 19th century. subsequent excavations in the early 20th century revealed the stupa’s relics and inscriptions.
During excavations, stone relic caskets containing bone fragments, beads, and coins were uncovered, along with inscriptions in the Bhattiprolu Brahmi script. These findings confirmed the site’s connection to the early spread of Buddhism in South India. It is role as a significant religious and cultural hub.
Restoration Efforts and Present-Day Status
The Bhattiprolu Stupa has undergone several restoration efforts over the years to preserve its historical and archaeological value. While much of the original structure has been damaged or lost over time, efforts by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) have helped restore parts of the stupa to its former glory.
Today, Bhattiprolu Stupa stands as a protected monument and attracts visitors interested in India’s Buddhist heritage. Although not as famous as other Buddhist stupas like Sanchi or Amaravati, Bhattiprolu holds a special place in the history of Buddhism and script development in India.
Also Read: Exclusive of the Guntupalli Buddhist Caves: In Andhra Pradesh
Today, Bhattiprolu Stupa stands as a protected monument and attracts visitors interested in India’s Buddhist heritage. Although not as famous as other Buddhist stupas like Sanchi or Amaravati, Bhattiprolu holds a special place in the history of Buddhism and script development in India.
Legacy of the Bhattiprolu Stupa
The legacy of Bhattiprolu Stupa extends beyond its role as a religious monument. Its contribution to the development of the Brahmi script and its influence on South Indian culture and language make it a site of immense historical importance. For scholars of ancient Indian history and epigraphy. Bhattiprolu represents a critical link in understanding the cultural and linguistic evolution of South India.
For the local population and Buddhists worldwide, the Bhattiprolu Stupa in AP remains a symbol of the enduring legacy of the Buddha’s teachings and the rich cultural history of the region. The site continues to inspire awe and reverence for the ancient traditions that shaped the spiritual and intellectual life of India.
How to Reach Bhattiprolu Stupa
By Air:
The nearest airport to Bhattiprolu is Vijayawada Airport, about 60 kilometers away. From the airport, you can hire a taxi or take a bus to Bhattiprolu.
By Train:
Bhattiprolu has its railway station, which is well-connected to nearby cities. You can catch a train from Vijayawada or Guntur and reach Bhattiprolu easily.
By Road:
Good roads connect Bhattiprolu. You can take a bus or drive from nearby cities like Vijayawada (around 50 km) or Guntur (around 40 km). Local buses and taxis are available from these cities.
Nearby Places to Visit
- Amaravati Stupa (around 45 km)
A famous ancient Buddhist site with impressive carvings and relics. - Undavalli Caves (around 50 km)
Rock-cut caves with stunning sculptures and a large reclining Buddha statue. - Kondapalli Fort (around 75 km)
An ancient fort with panoramic views and a peek of medieval architecture. - Mangalagiri Temple (around 40 km)
A popular temple dedicated to Lord Narasimha, known for its unique rituals.
Conclusion
The Bhattiprolu Stupa is more than just an archaeological site; it is a symbol of the historical confluence of religion, culture, and language in ancient India. Its influence on the evolution of Buddhist architecture and South Indian scripts places it among the most significant Buddhist monuments in the country. Though lesser known, Bhattiprolu’s legacy endures as a reminder of the region’s rich Buddhist heritage and its contribution to India’s cultural tapestry. Visiting Bhattiprolu is like taking a journey back in time, where the echoes of an ancient civilization still resonate through the stupa’s relics and inscriptions, offering a glimpse into a world where spirituality, architecture, and language flourished in harmony.
Frequently Asked Questions
A: Bhattiprolu Stupa is known for being one of the earliest Buddhist stupas in South India and for its unique Brahmi script.
A: Bhattiprolu Stupa is located in Bhattiprolu village, Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh.
A: The best time to visit is during the winter months, from October to February.
A: Nearby attractions include Amaravati Stupa, Undavalli Caves, Kondapalli Fort, and Mangalagiri Temple.
A: Bhattiprolu Stupa was constructed during the Mauryan period, around the 3rd century BCE.