Amaravathi, a small yet historically rich village situated on the banks of the Krishna River in the Palnadu district of Andhra Pradesh, India, stands as a testament to India’s deep cultural and religious heritage. Known for its connections to both Hinduism and Buddhism, Amaravathi serves as a sacred site and a key archaeological treasure trove, blending ancient traditions with a modern-day resurgence in importance. Let’s explore this remarkable village and its layers of history, religion, and culture.

Historical Significance Amaravathi
Origins and Foundation
Amaravathi, as it exists today, was founded in the 1790s by Raja Vasireddy Venkatadri Nayudu. Who chose it as the capital of his state. He relocated from Chintapalli in protest against the British East India Company, marking the beginning of the village’s modern history. However, Amaravathi’s roots stretch far deeper into antiquity, with its name borrowed from the nearby ancient Amaravati Stupa. A significant Buddhist monument was unearthed during the village’s construction. The village also lies adjacent to Dhanyakataka (modern-day Dharanikota), the ancient capital of the Satavahana Dynasty.
Amaravati Stupa: A Buddhist Legacy
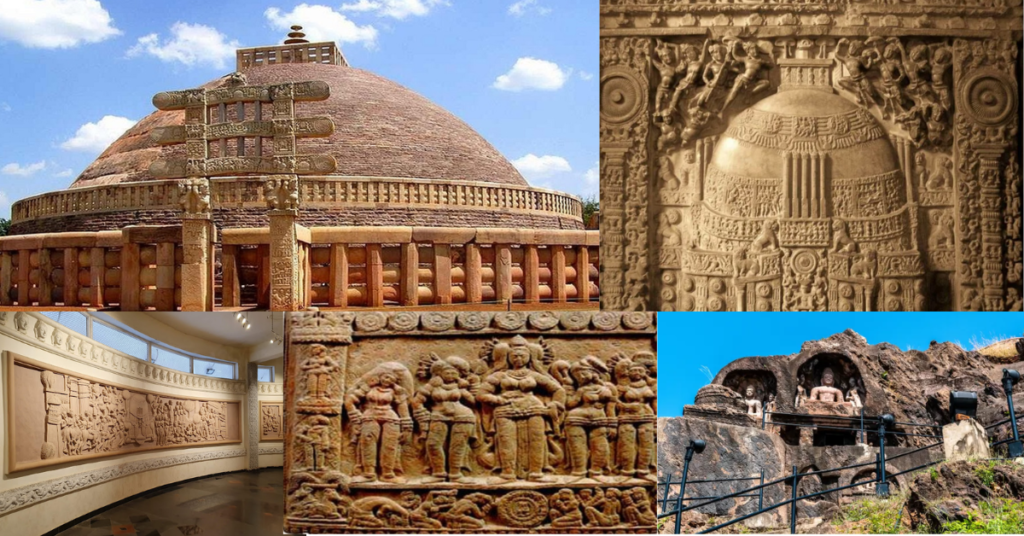

Amaravathi was a major center of Buddhism, and its most renowned monument is the Amaravati Stupa. Built between the 2nd century BCE and the 3rd century CE, it is one of the largest stupas in India. The stupa was constructed during the rule of the Satavahanas and later expanded during the time of the Ikshvaku Dynasty. Carvings on the stupa depict the life of the Buddha, and its significance in Buddhist art and architecture is unparalleled. It was an important site for the spread of Buddhism across South Asia, including Sri Lanka. Today, though much of the original stupa has been dismantled, it ruins. Along with artifacts excavated from the site, are preserved in museums such as the Amaravathi Heritage Centre and Museum.
Also Read: The Exclusive of Sri Bhavanarayana Swamy Temple in Sarpavaram
Cultural and Religious Importance of Amaravati
A Sacred Site for Hindus
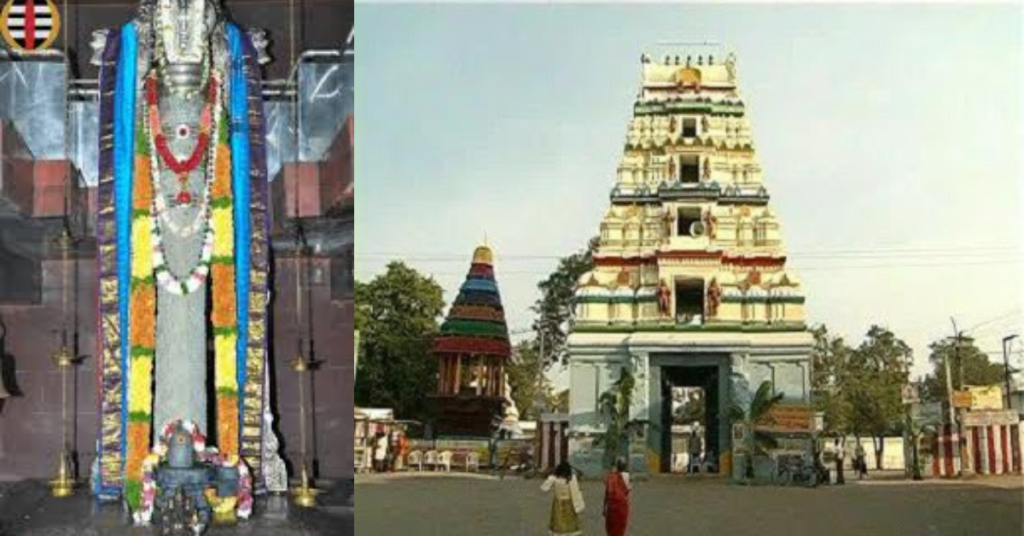

Amaravathi is also a sacred site for Hindus. The Amaralingeswara Temple, dedicated to Lord Shiva, is one of the Pancharama Kshetras—five sacred temples dedicated to Shiva in Andhra Pradesh. The temple has been a pilgrimage site for centuries, drawing devotees from across the region. It plays a central role in the town’s religious life, with important festivals such as Mahashivaratri and Navaratri celebrated with grandeur.
Kalachakra Tantra and Buddhist Revival
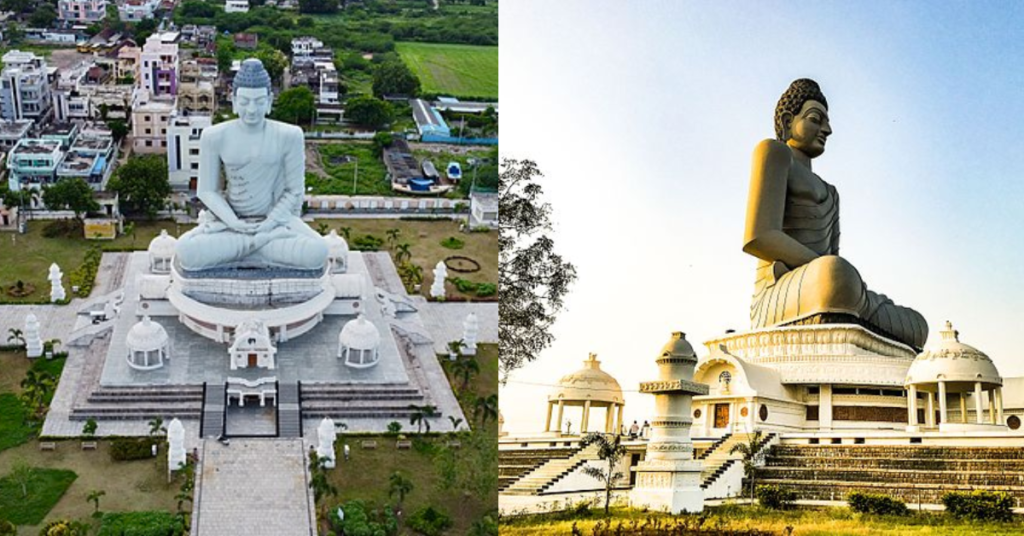

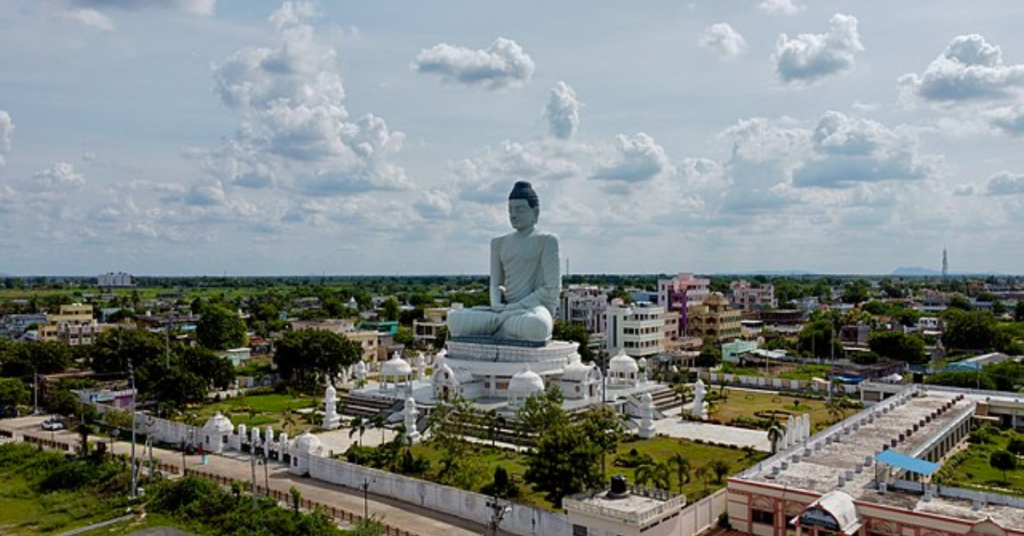
Buddhism, once dominant in the region, saw a revival in modern times. Gautama Buddha is said to have visited Dhanyakataka (Amaravathi), and according to tradition, he delivered sermons in the region. In recent years, Amaravathi has hosted significant Buddhist events, such as the 30th Kalachakra Festival in 2006, presided over by the Dalai Lama. The village also features a 125-foot-tall statue of Buddha in the Dhyana (meditative) posture. A symbol of its enduring connection to Buddhist teachings.
Also Read: Exclusive of the Guntupalli Buddhist Caves: In Andhra Pradesh
Artwork and architecture
Amaravathi School of Art
Amaravathi was a major center of the Amaravati School of Art. A unique art tradition that developed between the 1st and 3rd centuries CE during the Satavahana period. The art from this region is characterized by intricate carvings, bas-reliefs, and stone sculptures that often depict key episodes from the Buddha’s life. The artistic styles from Amaravathi influenced Buddhist art across South Asia, and many of its sculptures were exported to places like Sri Lanka.
Skanda Purana and Other Texts
The importance of Amaravathi in Hindu culture is also documented in sacred texts like the Skanda Purana. Which describes the Amaralingeswara Temple and its significance in Shiva worship. The temple’s design and structure showcase traditional South Indian architecture with intricate carvings and an imposing Shiva lingam.
Government and Politics
Amaravathi falls under the Pedakurapadu Assembly constituency, and its present MLA is Bhashyam Praveen from the Telugu Desam Party (TDP). The local administration, through the gram panchayat, plays a crucial role in maintaining the village’s historical sites and managing its governance.
Modern Revival and Development
Amaravathi has witnessed efforts to revitalize its heritage under the Government of India’s HRIDAY (Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana) scheme as part of the Andhra Pradesh Capital Region. This initiative aims to preserve and enhance the town’s cultural significance by developing its infrastructure and promoting it as a center for tourism and pilgrimage.
How to Reach
By Air: The nearest airport is Vijayawada Airport, which is about 52 km (32 miles) from Amaravati. From the airport, you can hire a taxi or take a bus to reach Amaravati.
By Train: The closest railway station is Vijayawada Railway Station, around 35 km (22 miles) away. From the station, you can take a taxi, bus, or auto-rickshaw to reach Amaravati.
By Bus: You can take a state or private bus to Vijayawada or Guntur. From there, you can take local buses or taxis to Amaravati, which is about 35 km from both cities.
Also Read: Exploring the Rich Avian Diversity of Uppalapadu Bird Sanctuary
Nearby Visiting Places
Undavalli Caves
About 30 km (18 miles) from Amaravati, these ancient rock-cut caves are known for their impressive carvings and beautiful statues, including a large reclining Vishnu.
Bhattiprolu Stupa
Located around 50 km (31 miles) from Amaravati, this ancient Buddhist stupa is believed to be one of the earliest examples of Buddhist architecture in South India.
Mangalagiri Temple
Situated around 22 km (14 miles) from Amaravati, this temple is dedicated to Lord Narasimha and is located on a hill, offering breathtaking views of the surrounding areas.
Kondaveedu Fort
Around 60 km (37 miles) away, Kondaveedu Fort is a historic hilltop fort with impressive ruins and scenic views. The Kondaveedu village is also famous for its handcrafted wooden toys.
Prakasam Barrage
Located in Vijayawada, about 35 km (22 miles) from Amaravati, this barrage across the Krishna River offers a picturesque view, especially during sunrise and sunset.
Vijayawada Kanaka Durga Temple
Situated on Indrakeeladri Hill in Vijayawada, this temple is dedicated to Goddess Durga and attracts many pilgrims due to its religious importance and panoramic views of the Krishna River.
Conclusion
Amaravathi stands as a unique confluence of India’s ancient Buddhist heritage and vibrant Hindu traditions. Its history, stretching over 2,300 years, bears witness to the rise of dynasties, the spread of religious teachings, and the evolution of art and architecture. Today, it is not only a spiritual destination for pilgrims of multiple faiths but also an important archaeological site. Reminding the world of India’s rich cultural heritage. As Amaravathi continues to evolve, balancing its historical importance with modern-day aspirations, it remains a symbol of India’s enduring legacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
A: Amaravati is famous for its ancient Buddhist Stupa and the Amaralingeswara Swamy Temple.
A: The Amaravati Stupa is an ancient Buddhist monument known for its intricate carvings, dating back to the 2nd century BCE.
A: Amaravati is situated on the banks of the Krishna River.
A: The Dhyana Buddha Statue is a 125-foot-tall statue of Buddha in a meditation posture.
A: Yes, Amaravati is a pilgrimage site for both Hindus and Buddhists.